Server-Side Rendering
The Server-Side Rendering (SSR) is the process of rendering web pages on a server and passing them to the browser (client-side): the HTML of the page is generated on the server for each request.
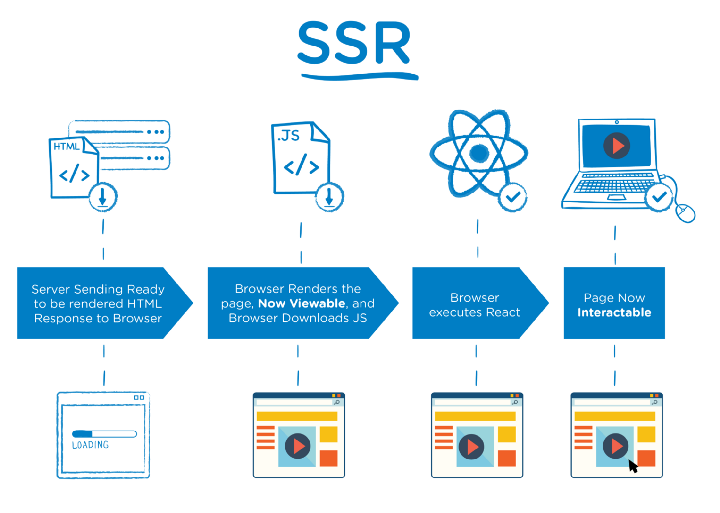
The generated HTML, JSON data, and JavaScript instructions are not making the page interactive.
On the client, the HTML is used to show a fast non-interactive page, while React uses the JSON data and JavaScript instructions to make components interactive (for example, attaching event handlers to a button). This process is called hydration.
In Next.js, we can opt to server-side render pages by using getServerSideProps() function.
Advantages
- Pages are rendered fast, even if the speed of the internet provider is not high.
- High level of SEO: the content of the pages is already loaded and, for this reason, get indexed more quickly than Client-Side Rendering.
- Pages can be cached.
Disadvantages
- The transition from one page to another takes more time, especially if the amount of data is big; it happens because of double rendering on both sides (servers and clients).
- The vulnerability that gives more chance for a surface attack.
- The cost of the server is usually higher because it needs to be more powerful than CSR due to the higher amount of work and traffic it needs to handle.
- Usually gets more complex caching and generally needs to rely on external services.
- Higher latency: if there are too many users on the website who make the same requests, the traffic speed can be very slow.
When to use Server-Side Rendering?
Although server-side rendering has enough disadvantages, it is widely used for developing new software. Here are some cases where it is used:
- When the future development of the web application will have pretty simple UI with a little number of pages and options.
- When the application has a little amount of dynamic data.
- When the “Read” preference of the app prevails over functionalities.
- When the application is designed for a small number of users.
